Builder Pane
A review of the functions available on the Builder pane.
Overview
The Builder pane is accessed under the View tab or by clicking the ![]() icon on the main toolbar.
icon on the main toolbar.
The Builder pane is used to create and edit trackable models, also called trackable assets:
Rigid Body assets are created for tracking rigid objects.
Skeleton assets are created for tracking human motions.
Trained Markerset assets are used to track objects that are neither rigid nor human skeleton templates.
When created, trackable models store the positions of markers on the target object and use the information to auto-label the markers in 3D space. During the auto-label process, a set of predefined labels are assigned to 3D points using the solver pipeline, and the labeled dataset is then used for calculating the position and orientation of the corresponding Rigid Bodies or Skeleton segments. Auto-labeling is not available for Trained Markersets.
The trackable models can be used to auto-label the 3D capture both in Live mode (real-time) and in the Edit mode (post-processing). Each created trackable model will have its own properties which can be viewed and changed under the Properties pane. If new Skeletons or Rigid Bodies are created during post-processing, the Take will need to be auto-labeled again in order to apply the changes to the 3D data.
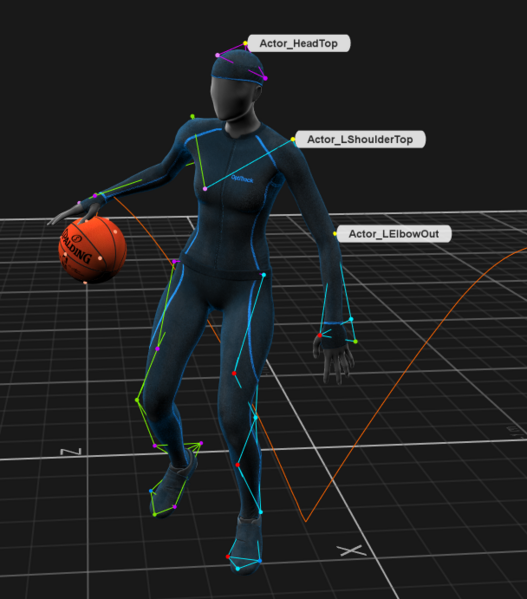
Interface Overview
On the Builder pane, you can either create a new trackable asset or modify an existing one. Select the Type of asset you wish to work on, and then select whether you wish to create or make modifications to existing assets. Create and Modify tools for different Asset types are explained in the sections below.
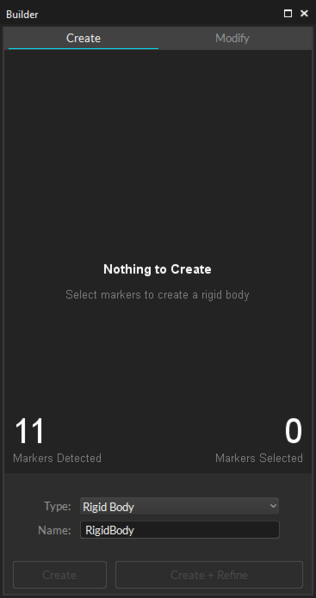
Post-Processing
Edit Mode is used for playback of captured Take files. In this mode, you can playback and stream recorded data and complete post-processing tasks, such as creating and modifying assets. The Cameras View displays the recorded 2D data while the 3D Viewport represents either recorded or real-time processed data as described below.
There are two modes for editing:
Edit: Playback in standard Edit mode displays and streams the processed 3D data saved in the recorded Take. Changes made to settings and assets are not reflected in the Viewport until the Take is reprocessed.
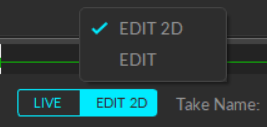
Edit 2D: Playback in Edit 2D mode performs a live reconstruction of the 3D data, immediately reflecting changes made to settings or assets. These changes are displayed in real-time but are not saved into the recording until the Take is reprocessed and saved. To playback in 2D mode, click the Edit button and select Edit 2D.
Regardless of the selected Edit mode, you must reprocess the Take to create new 3D data based on the modifications made.
Please see the Data Editing page for more information about editing Takes.
Defining Assets in Edit mode:
If the Rigid Bodies, or Skeletons, are created in Edit mode, the corresponding Take needs to be auto-labeled. Only then will the Rigid Body markers be labeled using the Rigid Body asset and positions and orientations be computed for each frame. If the 3D data have not been labeled after edits on the recorded data, the asset may not be tracked.
Rigid Body: Create
To create Rigid Bodies, select Rigid Body from the Type option and click the Create tab at the top. Here, you can create Rigid Body assets and track any markered-objects in the volume. In addition to standard Rigid Body assets, you can also create Rigid Body models for head-mounted displays (HMDs) and measurement probes as well
Tip: The recommended number of markers per Rigid Body is 4 ~ 12 markers.
You may encounter limits if using an excessive number of markers, or experience system performance issues when using the refine tool on such an asset.
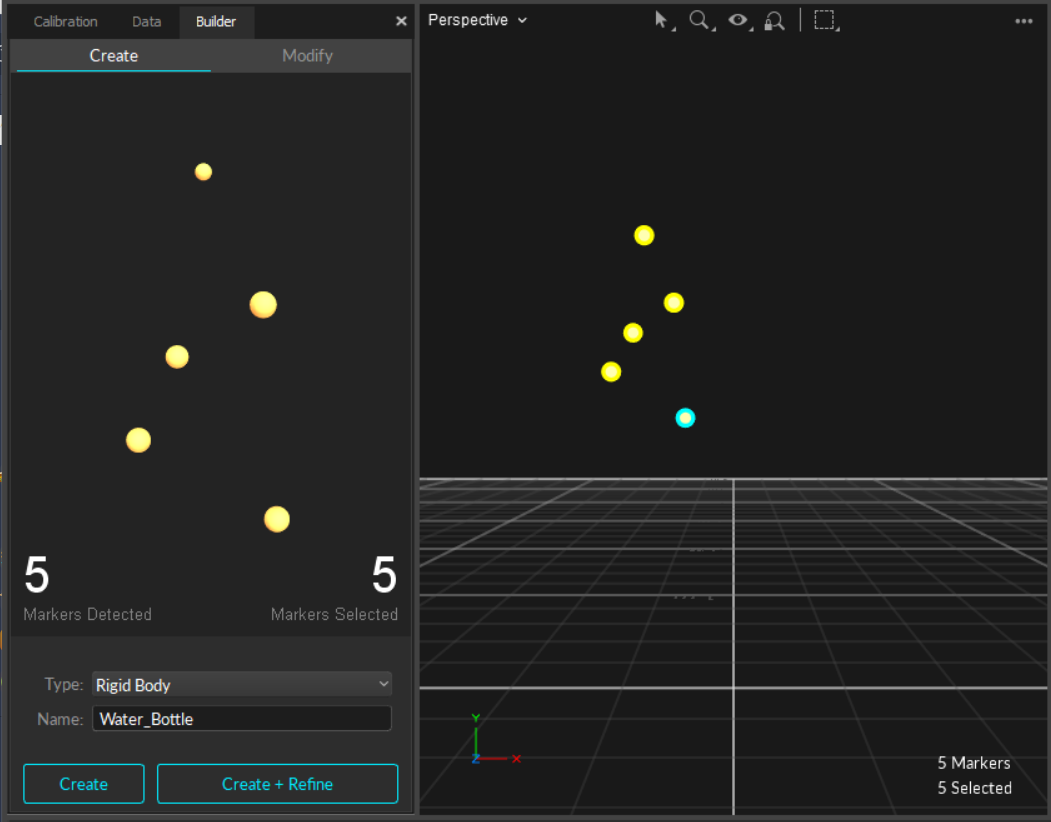
Create a Rigid Body
Select all associated Rigid Body markers in the 3D viewport.
On the Builder pane, confirm that the selected markers match those on the object you want to define as the Rigid Body.
Click Create to define a Rigid Body asset from the selected markers.
You can also create a Rigid Body using the following methods while the markers are selected:
Perspective View (3D viewport): Right-click on the selected markers to access the context menu. Under the Markers section, click Create Rigid Body.
Assets pane: While the markers are selected in Motive, click on the add
 button at the bottom of the Assets pane.
button at the bottom of the Assets pane.Hotkey: While the markers are selected, use the Create Rigid Body hotkey (Default: Ctrl +T).
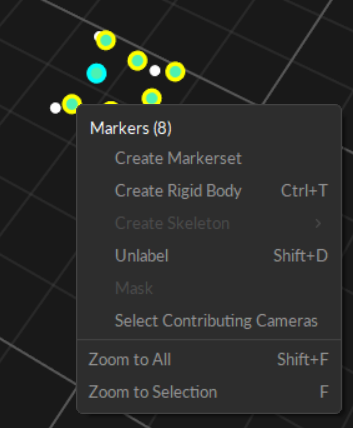
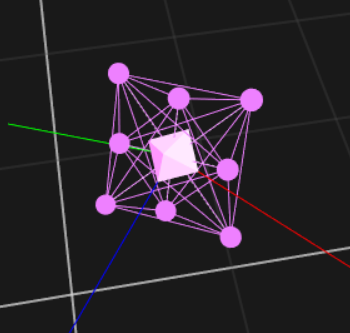
Once the Rigid Body asset is created, the markers will be colored, labeled, and interconnected to each other. The newly created Rigid Body will be listed under the Assets pane.
Create an HMD Rigid Body
Supported HMD Clips
Motive supports a variety of Head Mounted Display (HMD) clips, including VIVE Focus 3, Valve Index, and Varjo XR4, to name a few.
To see all supported clips or to add a custom clip to your configuration, browse to this folder on the Motive PC:
C:\ProgramData\OptiTrack\Motive\HMD

Create the HMD Rigid Body
For using OptiTrack system for VR applications, it is important that the pivot point of the HMD Rigid Body is placed at the appropriate location, at the root of the nose in between the eyes.
When using the HMD clips, you can utilize the HMD creation tools in the Builder pane to have Motive estimate this spot and place the pivot point accordingly. Motive uses known marker configurations on the clip to precisely position the pivot point and set the desired orientation.
HMDs with passive markers can utilize the External Pivot Alignment tool to calibrate the pivot point.

Make sure Motive is configured for tracking active markers.
Open the Builder pane under View tab and click Rigid Bodies.
Under the Type drop-down menu, select HMD. This will bring up the options for defining an HMD Rigid Body.
If the selected marker matches one of the Active clips, it will indicate which type of Active Clip is being used.
Under the Orientation drop-down menu, select the desired orientation of the HMD. The orientation used for streaming to Unity is +Z forward and Unreal Engine is +X forward, or you can also specify the expected orientation axis on the client plugin side.
Hold the HMD at the center of the tracking volume where all of the active markers are tracked well.
Select all 8 HMD active markers in the 3D viewport.
Click Create. An HMD Rigid Body will be created from the selected markers and it will initiate the calibration process.
During calibration, slowly rotate the HMD to collect data samples in different orientations.
Once all necessary samples are collected, the calibrated HMD Rigid Body will be created.
Create a Measurement Probe Rigid Body
You can also define a measurement probe using the Builder pane. The measurement probe tool utilizes the precise tracking of OptiTrack mocap systems and allows you to measure 3D locations within a capture volume. For more information, please read through the Measurement Probe Kit Guide.

Creating a probe using the Builder pane
Open the Builder pane under the View tab and click Rigid Bodies.
Bring the probe into the tracking volume and create a Rigid Body from the markers.
Under the Type drop-down menu, select Probe. This will bring up the options for defining a Rigid Body for the measurement probe.
Select the Rigid Body created in step 2.
Place and fit the tip of the probe in one of the slots on the provided calibration block.
Note that there will be two steps in the calibration process: refining Rigid Body definition and calibration of the pivot point. Click the Create button to initiate the probe refinement process.
Slowly move the probe in a circular pattern while keeping the tip fitted in the slot, making a cone shape overall. Gently rotate the probe to collect additional samples.
After the refinement, Motive will automatically proceed to the pivot point calibration.
Repeat the same movement to collect additional sample data for precisely calculating the location of the pivot or the probe tip.
When sufficient samples are collected, the pivot point will be positioned at the tip of the probe and the Mean Tip Error will be displayed. If the probe calibration was unsuccessful, just repeat the calibration again from step 4.
Once the probe is calibrated successfully, a probe asset will be displayed over the Rigid Body in Motive, and live x/y/z position data will be displayed under the Probe pane.
Caution
The probe tip MUST remain fitted securely in the slot on the calibration block during the calibration process.
Do not press in with the probe since the deformation from compressing could affect the result.
Note: Custom Probes
It's highly recommended to use the Probe kit when using this feature. With that being said, you can also use any markered object with a pivot arm to define a custom probe in Motive, but when a custom probe is used, it may have less accurate measurements; especially if the pivot arm and the object are not rigid and/or if any slight translation occurs during the probe calibration steps.
Rigid Body: Modify
The Builder pane has tools to modify the tracking of a Rigid Body selected in Motive. To do so, select a single Rigid Body from the Viewport or Assets pane and click the Modify tab to display the options for editing a Rigid Body.
Refine
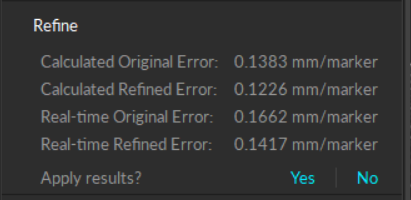
The Rigid Body refinement tool improves the accuracy of Rigid Body calculation in Motive. When a Rigid Body asset is initially created, Motive references only a single frame to define the Rigid Body. The Rigid Body refinement tool allows Motive to collect additional samples to achieve more accurate tracking results by improving the calculation of expected marker locations of the Rigid Body as well as the position and orientation of the Rigid Body itself.
Steps
From the View menu, open the Builder pane, or click the
 button on the toolbar.
button on the toolbar.Click on the Modify tab.
Select the Rigid Body to be refined in the Asset pane.
To refine the asset in Live mode, hold the physical selected Rigid Body at the center of the capture volume so that as many cameras as possible can clearly capture the markers on the Rigid Body.
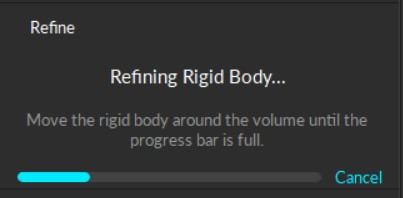
In the Refine section of the Modify tab of the Builder pane, click Start...
Slowly rotate the Rigid Body to collect samples at different orientations until the progress bar is full.
You can also refine the asset in Edit mode. Motive will automatically replay the current take file to complete the refinement process.
Probe Calibration
The Probe Calibration feature under the Rigid Body edit options can be used to re-calibrate a pivot point of a measurement probe or a custom Rigid Body. This step is also completed as one of the calibration steps when first creating a measurement probe, but you can re-calibrate it under the Modify tab.
Steps
In Motive, select the Rigid Body or a measurement probe.
Bring out the probe into the tracking volume where all of its markers are well-tracked.
Place and fit the tip of the probe in one of the slots on the provided calibration block.
Click Start.
Once it starts collecting the samples, slowly move the probe in a circular pattern while keeping the tip fitted in the slot, making a cone shape overall. Gently rotate the probe to collect additional samples.
When sufficient samples are collected, the mean error of the calibrated pivot point will be displayed.
Click Apply to use the calibrated definition or click Cancel to calibrate again.
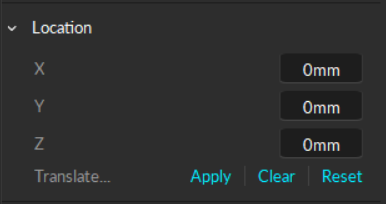
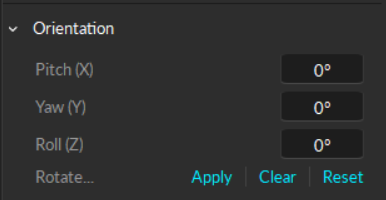
Location/Orientation
The Modify tab is used to apply translation or rotation to the pivot point of a selected Rigid Body. A pivot point of a Rigid Body represents both position (x,y,z) and orientation (pitch, roll, yaw) of the corresponding asset.
You can also use the Gizmo tools to quickly modify the pivot point of a Rigid Body.
Location
Use this tool to translate a pivot point in x/y/z axis (in mm). You can also reset the translation to set the pivot point back at the geometrical center of the Rigid Body.
Orientation
Use this tool to apply rotation to the local coordinate system of a selected Rigid Body. You can also reset the orientation to align the Rigid Body coordinate axis and the global axis. When resetting the orientation, the Rigid Body must be tracked in the scene.
OptiTrack Clip Tool
The OptiTrack Clip Tool recalibrates an HMD with OptiTrack HMD Clips to position its pivot point at an appropriate location. The steps are the same as when first creating the HMD Rigid Body.
Spherical Pivot Placement
This feature is useful when tracking a spherical object (e.g., a ball). It will assume that all of the markers on the selected Rigid Body are placed on a surface of a spherical object, and the pivot point will be calculated and re-positioned accordingly. Simply select a Rigid Body in Motive, open the Builder pane to edit Rigid Body definitions, and then click Apply to place the pivot point at the center of the spherical object.
Align To...
The Align To... section contains preset options for aligning the pivot point of a rigid body.
Click the ![]() button to see the options available:
button to see the options available:
Align to Geometry
The Align to Geometry feature provides an option to align the pivot of a rigid body to a geometry offset. Motive includes several standard geometric objects that can be used, as well as the ability to import custom objects created in other applications. This allows for consistency between Motive and external rendering programs such as Unreal Engine and Unity.
To use this feature, select the rigid body from the assets pane. In the Properties pane, click the ![]() button and select Show Advanced if it is not already selected.
button and select Show Advanced if it is not already selected.
Scroll to the Visuals section of the asset's properties. Under Geometry, select the object type from the list.
To import your own object, select Custom Model. This will open the Attached Geometry field. Click on the file folder icon to select the .obj or .fbx file to import into Motive.
Align to Camera
To align an asset to a specific camera, select both the asset and the camera in the 3D Viewport. Click Camera in the Align to... field in the Modify tab.
Align to Rigid Body
To align an asset to an existing Rigid Body, you must be in 2D edit mode. Click the Edit button at the bottom left and select EDIT 2D from the menu.
The asset you wish to align must be unsolved. If necessary, right-click on the asset in the Assets pane and select Remove Solve from the context menu.
Once the asset is unsolved, select it in the 3D Viewport, then select the rigid body that you wish to align it to. Once both assets are selected, click Rigid Body in the Align To... field.
Align to Marker
The Align to Marker feature sets the pivot point at the location of a specific marker. To use, select the asset from the Assets pane, select the marker you wish to align the pivot point with, then select Align To...Marker.
Make sure only 1 marker is selected for proper alignment.
To align the pivot point between a subset of markers, use the Gizmo Tool.
Align to Origin
Stationary rigid bodies can be used to maintain a consistent global origin for a mocap volume. Once the pivot point of a rigid body is aligned to the origin, you can use that rigid body to set world origin each day. This option is also helpful if you do not have easy access to the floor.
Before using this feature, make sure the system has an exceptional calibration.
Once you have the desired calibration, select the rigid bodies you wish to align then select Align To...Origin.
Reset Pivot
The Reset Pivot feature returns the pivot point to the default location.
Asset Dropdown Menu
By default, the Modify tab of the Builder pane is locked to the asset selected in the 3D Viewport. To change the asset from the Builder pane instead, click the ![]() icon at the top of the Modify tab to unlock the drop-down list.
icon at the top of the Modify tab to unlock the drop-down list.

To work with Marker Constraints and/or Marker Sticks, you must select the items you wish to modify in the 3D viewport.
Skeleton: Create
Skeleton tracking requires a Motive:Body or Motive:Body - Unlimited license.
From the Create tab, select the Skeleton option from the Type dropdown menu. This allows you to select the Skeleton Marker Set to use, choose the calibration pose, and create the Skeleton model.
Select a Template
Select a Skeleton Marker Set template from the Template drop-down menu. The Builder pane will display a Skeleton avatar that shows where to place the markers on the subject for the selected template.
When the 6 Rigid Body Skeleton template is selected, the display shows where to place the rigid bodies.
Right-click and drag the mouse to rotate the model view to see other angles.

Place Markers on Actor
Refer to the avatar and place the markers on the subject accordingly. For accurate placement, ask the subject to stand in the calibration pose while attaching the Skeleton markers. It is important to place markers at the right locations on the subject's body for the best Skeleton tracking. The markers on the avatar are color coded:
Green markers are placed on select joints, such as the elbows and knees, where precise placement is critical for proper skeleton calibration when using the full Range of Motion calibration method.
White markers are placed on the remaining joints, such as the shoulders and hips. These markers should also be placed in the precise location shown.
Magenta markers are segment markers that can be placed at a slightly different position within the segment to distinguish one skeleton from another.
Confirm Marker Placement
Double-check the marker counts and their placements. It may be easier to use the 3D viewport in Motive to do this. The Builder pane will track the detected markers.
In the Builder pane, the Create and Create + Refine buttons become active once the number of Markers Needed and Markers Detected match, If Skeleton markers are not automatically detected, manually select them from the 3D perspective view.

Select Pose
Under the Pose section drop-down menu, select the desired calibration pose for defining the Skeleton. This is set to the T-pose by default. Note that the image in the Builder pane remains in A-pose regardless of the selection.
You have the option to calibrate the Skeleton with a full range of motion (ROM) during creation. See the Create and Refine Skeleton section, below, for more details.
Select Constraints
The reconstructed 3D markers that comprise an asset are known as constraints in Motive. Skeleton templates include pre-defined labels that correspond to the marker's location and easily import into other pipelines for biomechanical analysis or animation. Set Constraints to Default to use these pre-defined labels.
To import a custom XML file, select Choose File... then browse to the file location. See the Constraints XML Files page for more information on using custom constraints.
Constraints can be relabeled using the Constraints pane after the Skeleton is created.
Select Model
Motive includes two spine models for skeletons:
The Classic model has two spine bones and one neck bone. This is the traditional model still used in many production workflows.
The 7 Segment Spine model has five spine bones and two neck bones. This model accounts for the natural curves in the human spine and allows for better alignment between the Skeleton in Motive and the actor.

The 7 Segment Spine is the default model. To change the default, to go Settings > Assets. On the Assets tab under Skeleton Creation, change the Spine Type to the preferred default for your workflow.
Select Visual
Select how the Skeleton will display in the 3D perspective view.
None: Displays only constraints and marker sticks.
Segment: Displays Skeleton as individual Skeleton segments.
Avatar (male): Displays Skeleton as a male avatar.
Avatar (female): Displays Skeleton as a female avatar.
Cycle Avatar: Motive assigns one of the two gendered avatars at random.
The visual can be changed after the skeleton is created in the Skeleton properties.
Name the Skeleton
Assign a Name to the skeleton. Motive will use this name as a prefix when creating skeleton marker labels. You can also assign custom labels during Skeleton creation by loading a previously prepared Constraints XML file, as noted above, or by relabeling the constraints from the Constraints pane after the Skeleton is created.
Create Skeleton
Ask the subject to stand in the selected calibration pose. Standing in a proper calibration posture is important because the pose of the created Skeleton will be calibrated from it. For more details, read the calibration pose section of the Skeleton Tracking page.
Click Create to create the Skeleton without a full range of motion calibration. Once the Skeleton model has been defined, confirm all Skeleton segments and assigned markers are located at expected locations. If any of the Skeleton segments seem to be misaligned, delete and create the Skeleton again after adjusting the marker placements and the calibration pose.
In Edit Mode
If you are creating a Skeleton in the post-processing of captured data, you will have to auto-label the Take to see the Skeleton modeled and tracked in Motive.
Create and Refine Skeleton - Range of Motion
To calibrate the skeleton with a full range of motion during creation, click the Create + Refine button.
Range of Motion Take Files
By default, a Take with the name of the subject is recorded each time a Range of Motion calibration is completed in Live mode. This allows you to easily reprocess the skeleton if needed.
To turn this setting off, go to Settings > Assets. On the refinement tab, disable the Record ROM setting.
The Take is saved in the currently open data folder. If completing the ROM in edit mode, no additional recording is made.
Range of Motion Settings
The Assets tab of the Settings panel has settings that pertain to skeleton creation.

The Height Marker setting ensures the solved skeleton matches the correct height for the actor.


The Assets tab of the Settings panel includes a new Refinement tab with numerous advanced settings related to the Range of Motion, including the option to Solve Constraints Only, or to Use Constraint Weights. You can change these settings to more accurately calibrate the results to the subject when necessary.


How to Complete a Range of Motion Calibration
Watch this video for a demonstration of how to complete a full Range of Motion. The steps are detailed, below.
The Builder pane will display the ROM calibration settings. Have the subject stand in the middle of the volume in either a T-pose or an A-pose.

To see a list of recommended poses for the calibration, click the ![]() help button:
help button:

When ready, click Start.
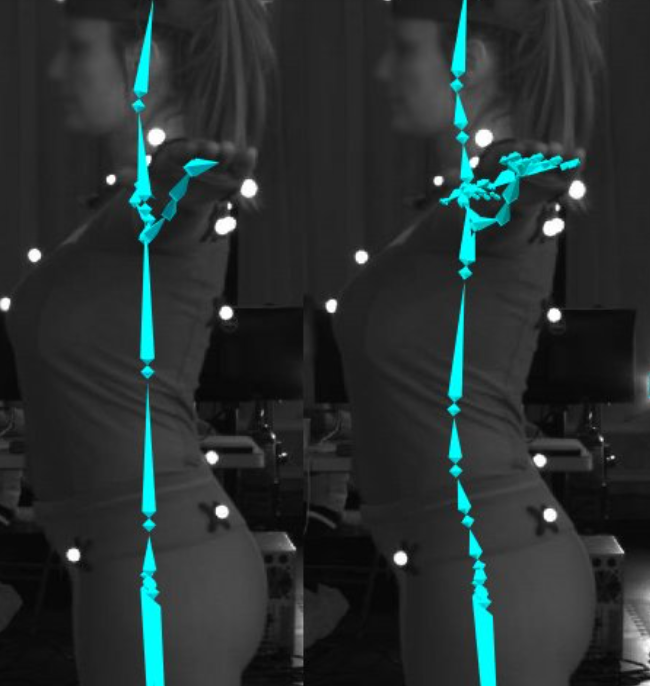
The Skeleton will appear in the 3D Viewport with the selected visual. Each bone segment will have a dark green hue at the beginning of sample collection.
Pro Tip: You can assign a hotkey on the keyboard to the function "Create and Refine Skeleton" to create a skeleton and begin the Range of Motion calibration with a single keystroke. See Settings: Mouse and Keyboard for instructions on assigning a hotkey.
The builder pane shows the progress for each bone segment. This helps identify which body parts the subject needs to move for the best calibration.

You can see which segments have sufficient samples and which need more in the "Coverage" bar in the Builder pane. Additionally, the bone segment will turn bright green in the 3D Viewport.

Note that the Start Calculation button appears early in the sample collection process. We recommend waiting until the coverage is complete for all bone segments before you begin calculating. However, if you are finding it difficult to achieve 100% coverage, and feel satisfied with the samples collected, you can click the Start Calculation button at any time after it appears.

When Motive has collected sufficient samples for all bone segments, the Builder pane and the Skeleton will change from green to blue.

The updated color reflects the quality of the calibration for that bone segment:

The calculation can take several minutes to run. When it completes, the results will display at the bottom of the Builder pane.

If you are satisfied with the results, click Apply. Otherwise, click Cancel.
If you cancel the Range of Motion calculation instead of applying it, Motive will create the skeleton, calibrated to the initial calibration pose. Use the Refine feature in the Modify tab of the Builder pane to apply a new Range of Motion calibration to the existing skeleton.
Once the ROM calibration is applied, the Builder pane will momentarily display "[skeleton name] Created." The skeleton will appear in the 3D Viewport using the visual selected during creation.

The Refinement section of the Skeleton's Properties shows the date, time, quality, and constraint error of the Range of Motion applied to the skeleton.


Skeleton: Modify

Update From Selection
This function recalibrates existing Skeleton assets using the current Skeleton information. The update will be based on a single T-pose frame. To calibrate the skeleton using a full Range of Motion (ROM), use the Refine feature instead.
To recalibrate a Skeleton, select all of the associated Skeleton markers from the perspective view. Make sure the selected Skeleton is in a calibration T-pose, and click the ![]() button to see the available options.
button to see the available options.
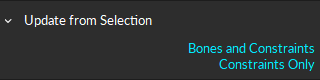
Bones and Constraints: This option recalibrates the selected skeleton using the same Skeleton Marker Set and refreshes the constraint locations. This can also be done using the Ctrl + R hotkey.
Constraints Only: This options recalibrates the selected skeleton's constraints based on the current location of the markers, without recalibrating bones.
You can also update the skeleton from the context menu in the Assets pane or in the 3D Viewport.
Skeleton recalibration does not work with Skeleton templates that include additional markers.
Refine
The Refine function allows you to apply a Range of Motion (ROM) calibration to a skeleton anytime after it's been created, including in post-production. See the section Create and Refine Skeleton - Range of Motion for details on how to use to use this tool.
Motive has the option to save a backup copy of the original skeleton for comparison purposes when completing a Live Range of Motion calibration on an existing skeleton asset. To turn this setting on, go to Settings > Assets and enable the setting Save Unrefined Skeleton on the Refinement tab.
Trained Markersets: Create
Users can create assets from any object that is not a Rigid Body or a pre-defined Skeleton using the Trained Markersets feature. This article will cover the basics of creating and modifying a Trained Markerset asset from the Builder pane. Please refer to the Trained Markersets article for more information on using this feature.

Steps
Attach an adequate number of markers to your flexible object. This is highly dependent on the object but should cover at least the outline and any internal flex points. e.g., if it's a mat, the mat should have markers along the edges as well as dispersed markers in the middle in an asymmetrical pattern.
Record the movements you want of the object, trying to get as much of the full range of motion as possible.
In Edit mode, select the markers attached to the object.
From the Create tab of the Builder pane, select Markerset as the Type. Name the asset, then click Create from Selection.
Trained Markersets: Train and Modify
Once the asset is created, use the Training function so Motive can learn the object's full range of motion and how it moves through 3D space. Click Train from Take then playback the .tak file created in step 2 of the asset creation. Use the Clear button to remove the asset's existing training.
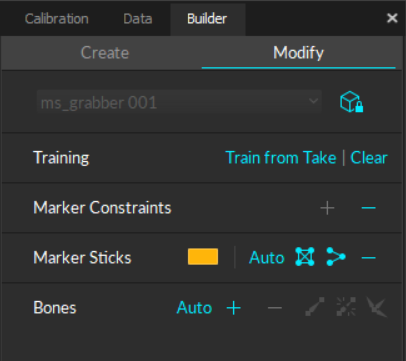
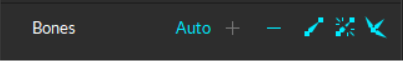
Bones
In Motive, a Bone is a virtual structure that connects two joints and represents a segment of a virtual skeleton or Trained Markerset. To access these functions, select either the entire asset (to use the auto-generate option), or select the specific markers or bones that you would like to modify in the 3D Viewport.
![]()
Auto-generates bones at flex points for the selected asset.
![]()
Adds (+) or Removes (-) the selected bone(s).
![]()
Adds a bone chain between two selected bones. Whichever bone is selected first becomes the parent bone, the second becomes the child bone.
![]()
Unparents the selected bone or bones. This removes the bone chain between the bones.
![]()
Reroots the selected child bone and makes it the parent in the bone chain.
Marker Constraints
You can add or remove marker constraints (referred to as asset model markers in version 3.0 and earlier) from an asset using the Builder pane.
Steps
From the Viewport visual options, enable selection of Marker Constraints.
Access the Modify tab on the Builder pane.
Select the asset whose marker constraints you wish to modify.
in the 3D Viewport, CTRL + left-click on a marker constraint that's associated with the selected asset. Click the
 button to add the marker constraint to the asset definition. To remove it, click the
button to add the marker constraint to the asset definition. To remove it, click the  button.
button.On the Marker Constraints section of the Builder pane, click + to add the marker to the definition or - to remove the marker.
Use the Constraints pane to modify marker label and/or colors.
Marker Sticks
Motive includes the ability to modify Marker Sticks for all asset types, directly from the Builder pane. Select two or more of the asset's markers in the 3D Viewport to activate this tool set.
![]()
Changes the color of the selected Marker Stick(s).
![]()
Autogenerates Marker Sticks for the selected Trained Markerset asset.
![]()
Connects all of the selected Markers to each other.
![]()
Creates Marker Sticks based on the order in which the markers were selected.
![]()
Removes the selected Marker Stick(s).
Last updated
Was this helpful?

