External Device Sync Guide: eSync 2
Overview
External Device Synchronization
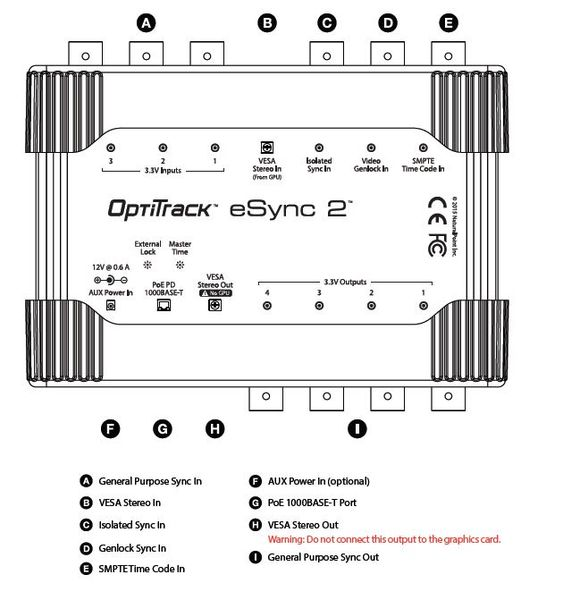
The eSync 2
Synchronization Setup
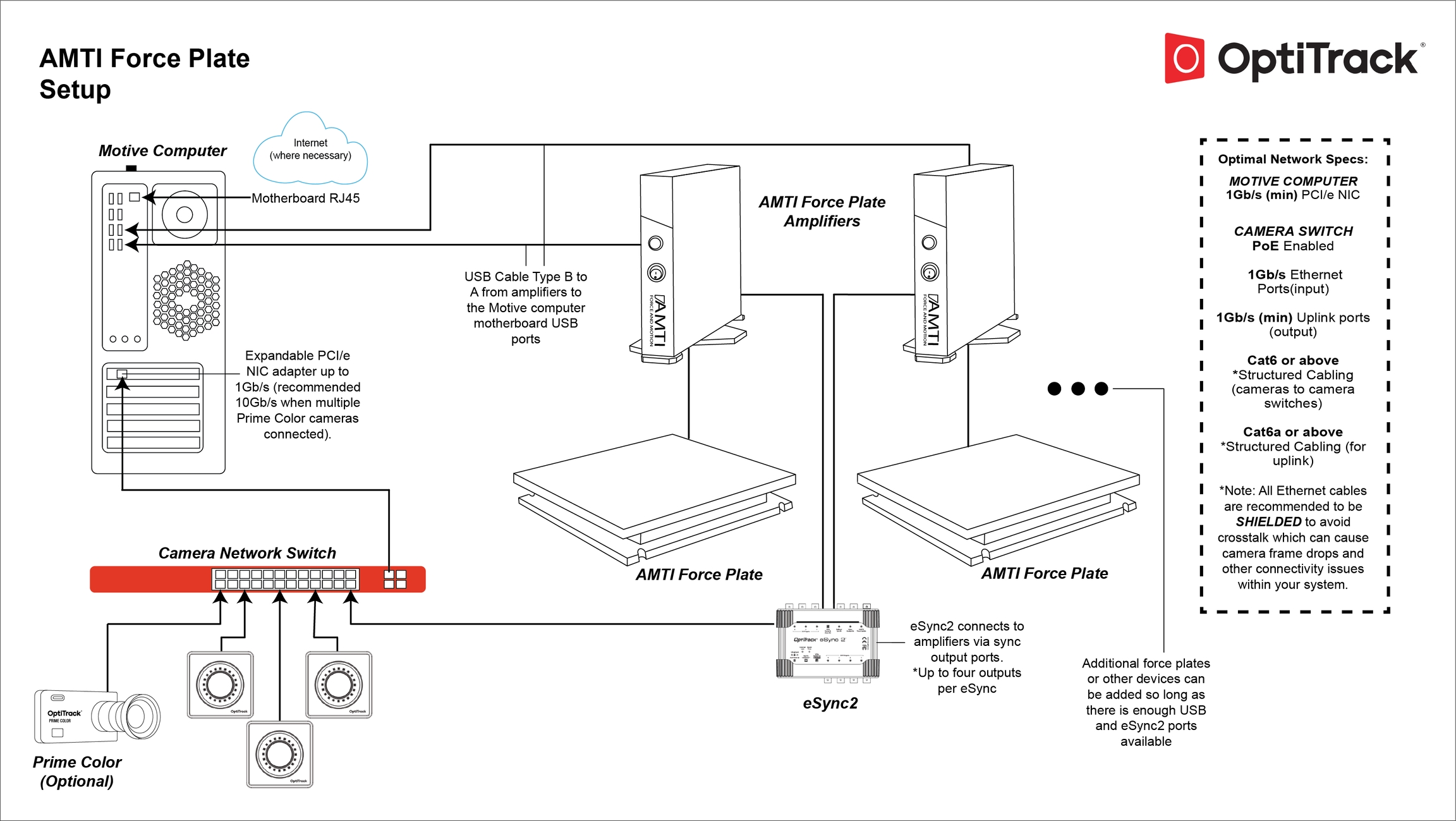
Step 1. Before setting up, draw out the schematic of which devices will be the parent or the child of the synchronization chain in respect to the mocap system.
Step 2. Connect the external devices
Step 3. Launch Motive. The eSync 2 should get listed under the Devices pane.
Step 4. [Motive] Open the Properties pane and select the eSync 2 in the Devices pane to access its properties.
Step 5. [Motive > Properties: eSync 2] Under the Sync Input Settings: Source section, use the drop-down menu to pick a desired sync source for the camera system to synchronize to. Read more under the Input Source Setup section of this page.
Step 6. [Motive > Properties: eSync 2] Configure the input divider/multiplier settings, and/or the clock frequency settings (for Internal Clock only), to set the camera rate. The final frame rate of the camera system will be displayed next to Camera Rate property or in the Devices pane.
Step 7. [Motive > Properties: eSync 2] Configure the Outputs. Output ports of the eSync 2 are used to tell connected child devices what Motive is doing. Read more under the Output Signal Setup section of this page.
Step 8. [Motive > Properties: eSync 2] If you wish to set up a recording trigger device, connect it to one of the input ports and designate the port under the Recording Trigger section of the eSync 2 properties. Read more under the Recording Trigger Setup section of this page.
Step 9. [Motive > Properties: eSync 2] Lastly, check the Monitor section and make sure all signals are detected properly.
Input Source Setup
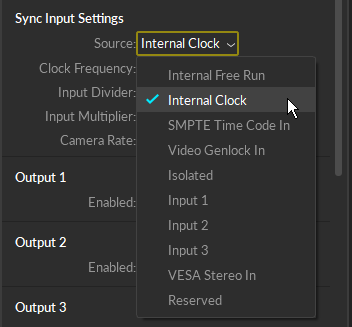
Sync Input: Select the Sync Source
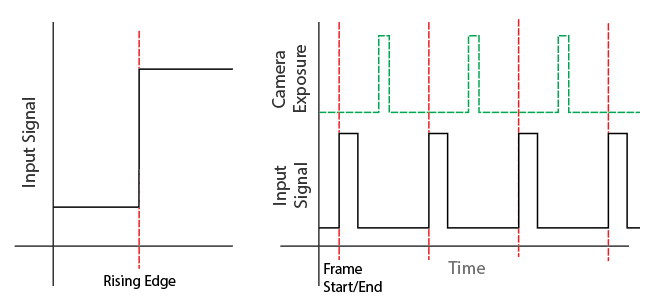
Sync Input: Set the Input Trigger
Rising Edge:
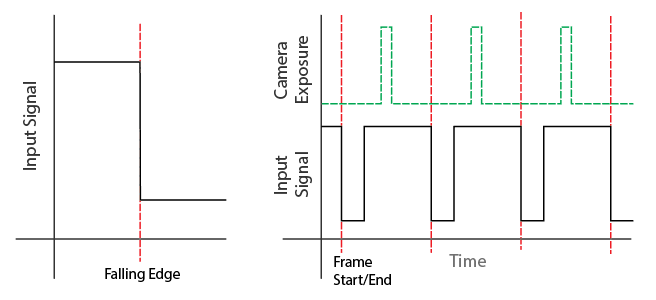
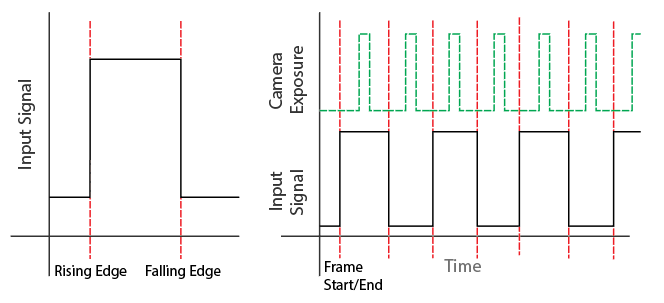
Set the Input Divider/Multiplier
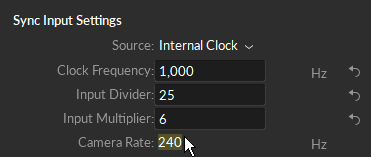
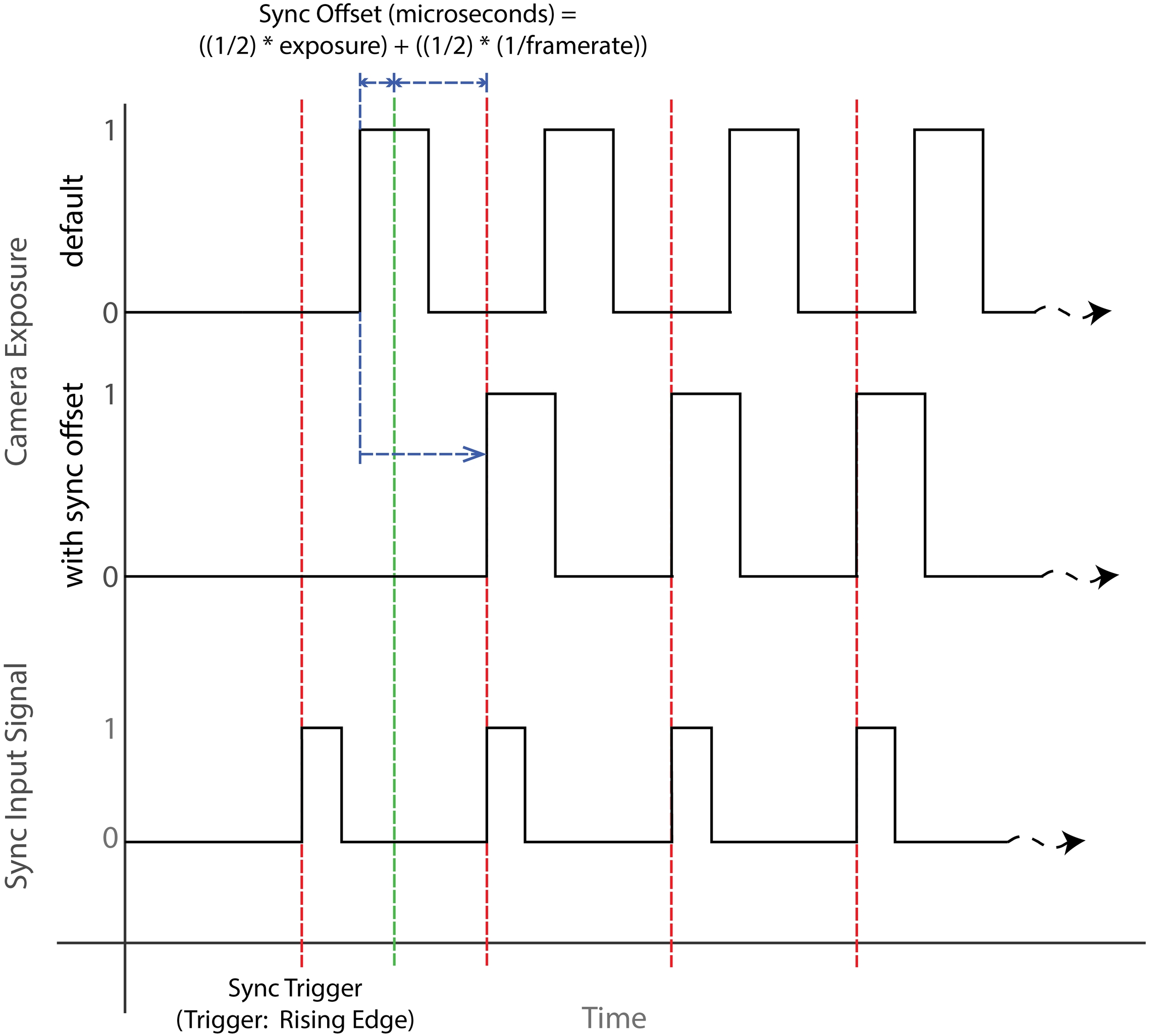
Set Sync Offset
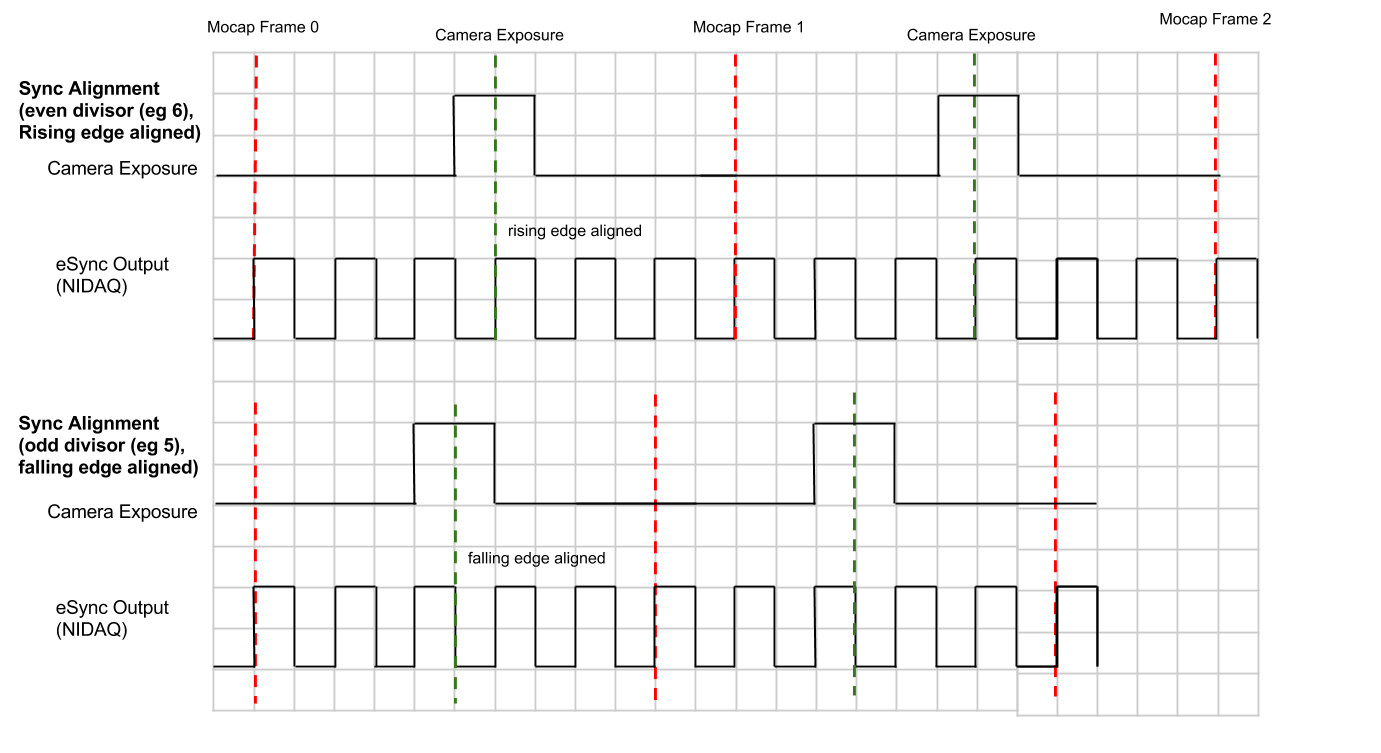
Advanced: Sync Input Trigger and Exposure Timing
Output Source Setup

Gated Output Signal (eSync 2):
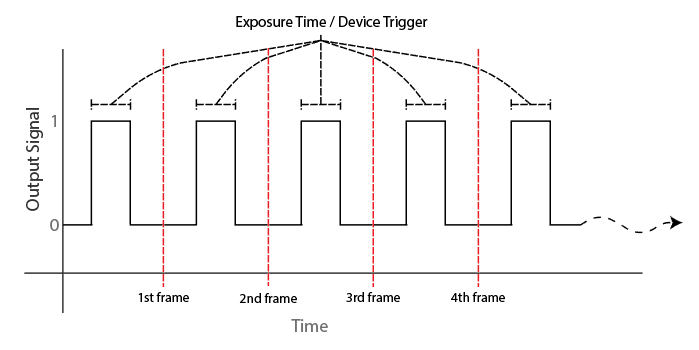
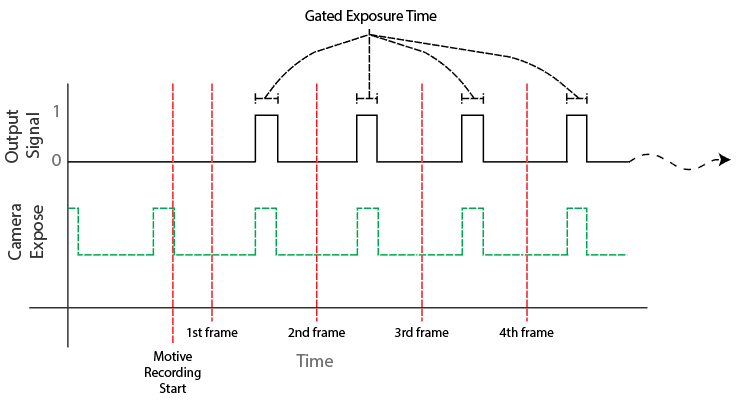
Exposure Time / Gated Exposure Time
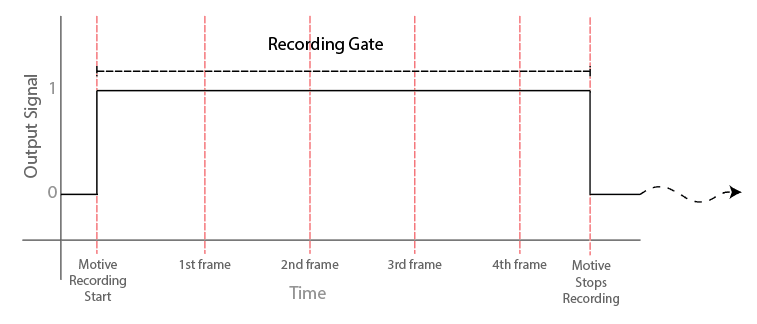
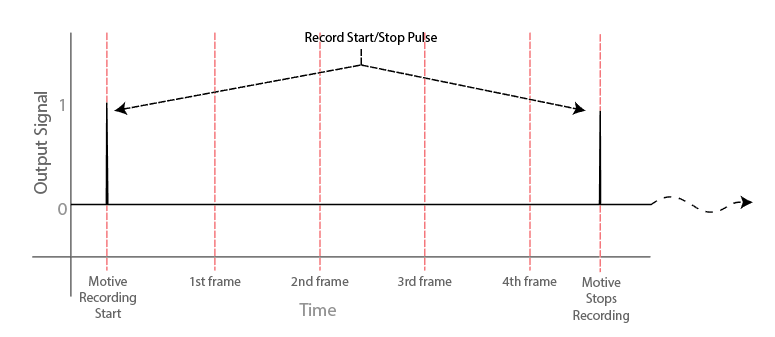
Recording Gate & Recording Start/Stop Pulse
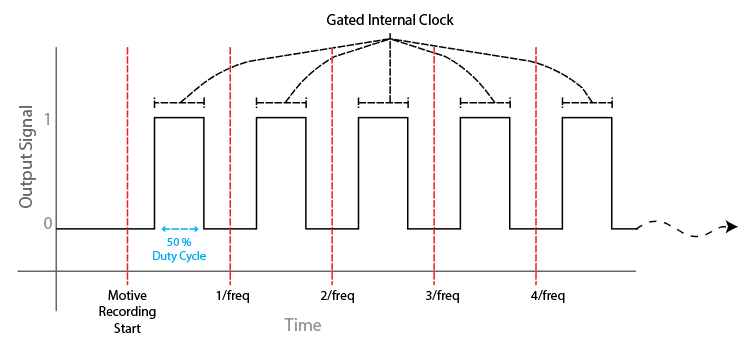
Gated Internal Clock
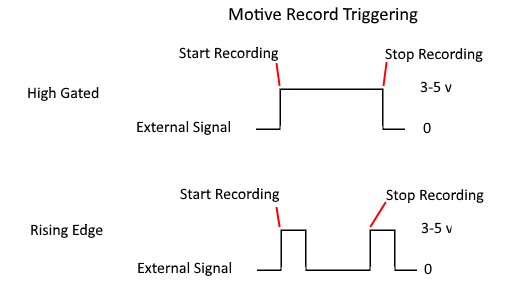
Hardware Recording Trigger Setup
Troubleshooting
Was this helpful?

