Transforming Coordinate System: Global to Local
The API reports "world-space" values for markers and rigid body objects at each frame. It is often desirable to convert the coordinates of points reported by the API from the world-space (or global) coordinates into the local space of the rigid body. This is useful, for example, if you have a rigid body that defines the world space that you want to track markers within.
Rotation values are reported as both quaternions, and as roll, pitch, and yaw angles (in degrees). Quaternions are a four-dimensional rotation representation that provide greater mathematical robustness by avoiding "gimbal" points that may be encountered when using roll, pitch, and yaw (also known as Euler angles). However, quaternions are also more mathematically complex and are more difficult to visualize, which is why many still prefer to use Euler angles.
There are many potential combinations of Euler angles so it is important to understand the order in which rotations are applied, the handedness of the coordinate system, and the axis (positive or negative) that each rotation is applied about.
These are the conventions used in the API for Euler angles:
Rotation order: XYZ
All coordinates are *right-handed*
To create a transform matrix that converts from world coordinates into the local coordinate system of your chosen rigid body, you will first want to compose the local-to-world transform matrix of the rigid body, then invert it to create a world-to-local transform matrix.
To compose the rigid body local-to-world transform matrix from values reported by the API, you can first compose a rotation matrix from the quaternion rotation value or from the yaw, pitch, and roll angles, then inject the rigid body translation values. Transform matrices can be defined as either "column-major" or "row-major". In a column-major transform matrix, the translation values appear in the right-most column of the 4x4 transform matrix. For purposes of this article, column-major transform matrices will be used. It is beyond the scope of this article, but it is just as feasible to use row-major matrices by transposing matrices.
In general, given a world transform matrix of the form: M = [ [ ] Tx ] [ [ R ] Ty ] [ [ ] Tz ] [ 0 0 0 1 ]
where Tx, Tz, Tz are the world-space position of the origin (of the rigid body, as reported from the API), and R is a 3x3 rotation matrix composed as: R = [ Rx (Pitch) ] * [ Ry (Yaw) ] * [ Rz (Roll) ]
where Rx, Ry, and Rz are 3x3 rotation matrices composed according to:
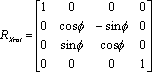
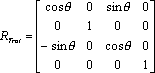
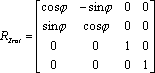
A handy trick to know about local-to-world transform matrices is that once the matrix is composed, it can be validated by examining each column in the matrix. The first three rows of Column 1 are the (normalized) XYZ direction vector of the world-space X axis, column 2 holds the Y axis, and column 3 is the Z axis. Column 4, as noted previously, is the location of the world-space origin. To convert a point from world coordinates (coordinates reported by the API for a 3D point anywhere in space), you need a matrix that converts from world space to local space. We have a local-to-world matrix (where the local coordinates are defined as the coordinate system of the rigid body used to compose the transform matrix), so inverting that matrix will yield a world-to-local transformation matrix. Inversion of a general 4x4 matrix can be slightly complex and may result in singularities, however we are dealing with a special transform matrix that only contains rotations and a translation. Because of that, we can take advantage of the method shown here to easily invert the matrix:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2624422/efficient-4x4-matrix-inverse-affine-transform
Once the world matrix is converted, multiplying it by the coordinates of a world-space point will yield a point in the local space of the rigid body. Any number of points can be multiplied by this inverted matrix to transform them from world (API) coordinates to local (rigid body) coordinates.
The API includes a sample (markers.sln/markers.cpp) that demonstrates this exact usage.
Last updated
Was this helpful?

